what is severe jaundice in babies
The yellowish appearance is a sign of an increased blood pigment called Bilirubin which then settles in the skinIn many cases this is a normal process and occurs in about 23 of all healthy newborns. Most infants born between 35 weeks gestation and full term need no treatment for jaundice.

Jaundice In Newborns Treatment And Care At Home
Jaundice also known as icterus is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and whites of the eyes due to high bilirubin levels.
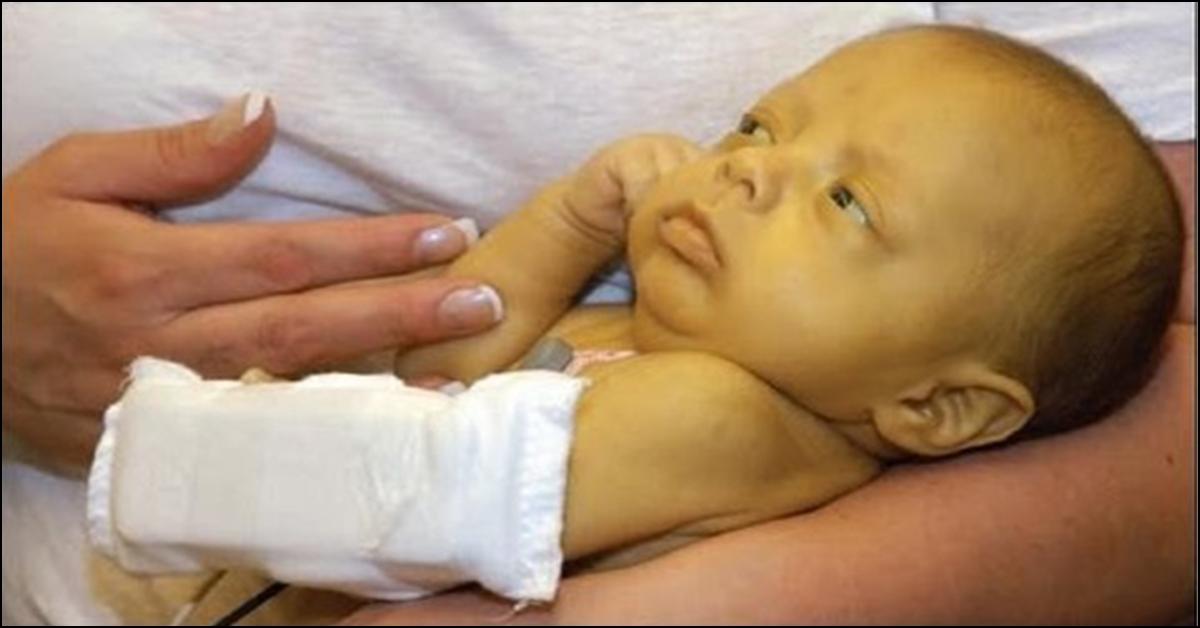
. When this happens babies are usually admitted to a newborn nursery. Exchange transfusion may also be prescribed in babies with extremely high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in the first 24 hours of life is considered pathological.
Deposition of bilirubin happens only when there is an excess of bilirubin a sign of increased production or impaired excretion. Jaundice is a medical condition where there is an excess of bile in the circulatory system. The prevalence of jaundice in adults is rare while jaundice in babies is common.
Jaundice is an emergency if the baby has a fever has become listless or is not feeding well. Your Baby Jaundice and Phototherapy. If jaundice is visible then a bilirubin level must be measured using a transcutaneous bilirubinometer or serum testing.
Kernicterus is a rare but serious complication of untreated jaundice in babies. If inadequately managed jaundice may result in severe brain injury or death. All babies Assess for risk factors Examine for jaundicevisualTcB Baby appears jaundiced.
Symptoms of jaundice include yellow discoloration of the eyes and skin light colored stools and more. About 60-80 of all term or late-term healthy newborns will develop some degree of hyperbilirubinemia1 The definition of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia has typically been total serum bilirubin TSB levels within the high-risk zone or greater than the 95th percentile. Visual estimation of the severity of jaundice is no longer acceptable.
The liver removes bilirubin from the blood and passes it. Jaundice may be dangerous in high-risk newborns. Risk factors for severe jaundice and higher bilirubin levels include premature birth before 37 weeks.
Occurs in 50 to 70 of term neonates. It affects both full-term and premature babies usually appearing during the first week of the babys life. A few babies will become deeply jaundiced and require investigation and treatment.
A serum bilirubin must be obtained in babies less than 35 weeks gestation or less than 24 hours old with visible jaundice. Most cases are physiological. Jaundice early detection is important Issue to note about jaundice.
Jaundice is generally NOT dangerous in babies who were born full term and who do not have other medical problems. Information about jaundice causes such as other diseases or conditions malaria hepatitis cirrhosis drugs cancer etc. Severe jaundice sometimes babies need treatment with more than one blue light at a time multiple phototherapy.
Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme metabolism liver dysfunction or biliary-tract obstruction. 6 March 2014 Neonatal jaundice. However in some babies bilirubin levels may rise excessively hyperbilirubinemia which can damage the brain cells.
Phototherapy is the use of visible light to treat severe jaundice in the neonatal period. Summarised recommendations replaced with full recommendations. This happens when there is too much bilirubin in the babys blood.
Approximately 60 of term babies and 85 preterm babies will develop clinically apparent jaundice which classically becomes visible on day 3 peaks days 5-7 and resolves by 14 days of age in a term infant and by 21 days in the preterm infant. Its caused by excess bilirubin damaging the brain or central nervous system. Jaundice occurs in approximately 60 per cent of newborns but is unimportant in most neonates.
Neonatal jaundice occurs in 60 of term infants and 80 of preterm infants 1 and is caused by hyperbilirubinaemia that is unconjugated divided into physiological or pathological or conjugated always pathological. Rarely and only in very severe cases where an underlying condition is causing the jaundice a blood transfusion may be needed. Babies born before 37 weeks or 85 months of pregnancy might have jaundice because their liver is not fully developed.
Jaundice in newborns is extremely common with 60 of full-term babies and 80 of preterm babies having the condition during the first week of lifeIn most cases jaundice does not present any complications and resolves itself over time. Jaundice happens when there is a high level of bilirubin a chemical present in liver bilehttpsmycl. Jaundice also known as hyperbilirubinemia is a frequently encountered clinical problem in neonates.
Jaundice which is also called hyperbilirubinemia is a condition often present in babies but the condition can also affect adults. Management Plot TSB on nomogram gestation weight and age appropriate for treatment regimen Treatmanage underlying disease Commence phototherapy as indicated Nutritionsupport breast feeding and adequate intake of formula. Coexisting severe mental illness and substance misuse.
Bilirubin bill-uh-ROO-bin is a yellow substance that comes from the normal breakdown of red blood cells. For moderate to severe jaundice a longer hospitalization stay will be warranted. Rarely an unusually high blood level of bilirubin can place a newborn at risk of brain damage particularly in the presence of certain risk factors for severe jaundice.
Jaundice is a common temporary. However the clinical presentation of. Some babies are more likely to have severe jaundice and higher bilirubin levels than others.
Neonatal jaundice is usually noted clinically when serum bilirubin is 855 micromolL 5 mgdL. And a mother with an O. Call the infants provider if.
Assessment and management in healthcare settings. Babies with any of the following risk factors need close monitoring and early jaundice management. Jaundice in a sibling.
In some babies an underlying disease may cause infant jaundice. 10 May 2016 Pathway updated and restructured in line with the partial update to NICEs guideline on jaundice in newborn babies under 28 days. Infant jaundice is a condition that occurs when a baby has elevated bilirubin levels causing their skin and eyes to have a yellowish tint.
Jaundice is severe the skin is bright yellow. Neonatal jaundice describes a condition in which an infants skin appears yellow within the first few days of life. And usually harmless condition in newborn infants.
East Asian or Mediterranean descent. Jaundice or hyperbilirubinemia in adults is caused by an underlying disease or condition. In newborn babies with very high levels of bilirubin in the blood hyperbilirubinaemia the bilirubin can cross the thin layer of tissue that separates the brain and blood the blood-brain barrier.
Jaundice is t he yellow colouring of skin and sclera caused by the accumulation of bilirubin in the skin and mucous membranes. The normal serum levels of bilirubin are less than 1mgdl. Babies with jaundice have a yellow coloring of the skin and eyes.
Jaundice also known as hyperbilirubinemia1 is a yellow discoloration of the body tissue resulting from the accumulation of an excess of bilirubin. Some of the symptoms of jaundice include yellowing of the whites of the eyes or skin rectal bleeding dark urine nausea vomiting weakness weight loss. Treatment for severe hyperbilirubinaemia includes phototherapy.
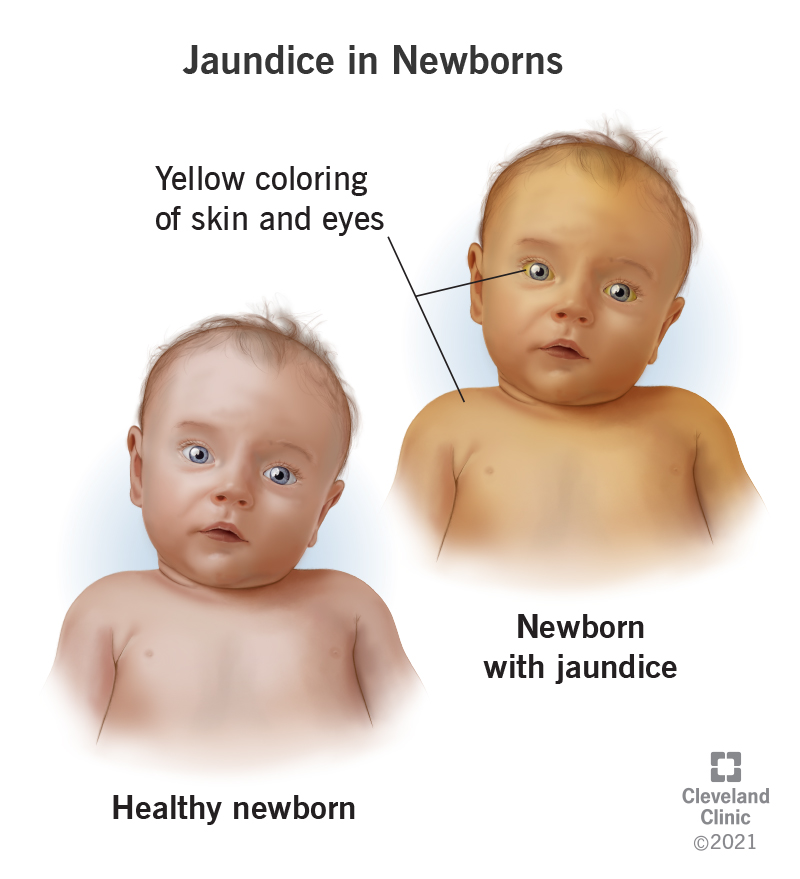
Jaundice In Newborns Symptoms Causes Treatment

Jaundice In Newborns Causes Symptoms And Treatment
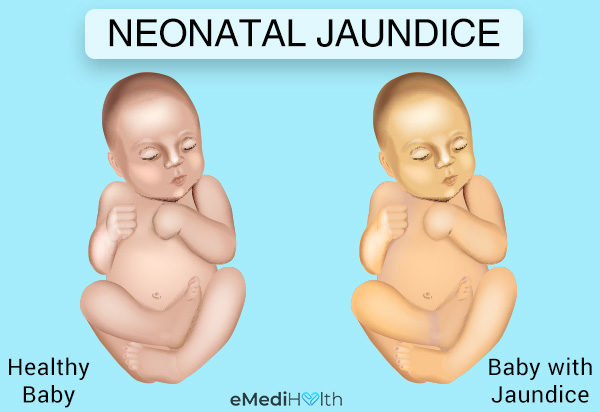
Jaundice In Newborns Treatment And Care At Home
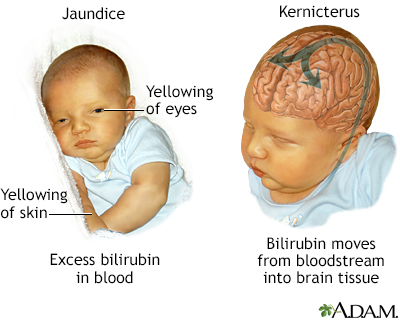
Bilirubin Encephalopathy Information Mount Sinai New York

Newborn Jaundice Birth Injury Guide

Newborn Jaundice Birth Injury Guide

Jaundice Is Common In Newborns Learn How To Spot The Signs Rocky Mountain Hospital For Children

